Overview of CUCM
Cisco Unified communication (UC) integrates voice, video, data, and mobility products and applications with an IP-based communications system. It makes communication more effective and secure and can change the way we communicate. UC represents a paradigm shift like the one of telegraph invention. By using voice, video, and data integration, UC eliminates the geographic barriers to effective communication. You can carry on business with an advancing and evolving fluidity. Information has long been at our fingertips, but UC enables knowledge and value to be shared by this information.
CISCO UC is an integrated solution comprising network infrastructure, security, mobility, products for network management, lifecycle services, flexible and outsourced management options, end-user, partner financing, and communication applications for third parties. By creating more effective communication, Cisco UC can dramatically change the business outlook without losing a personalized conversation. More effective communication leads to less time for commercialization and a quick and collaborative transformation of business processes.
Cisco UC Solution Components
The Cisco UC strategy includes the transmission of voice, video, and data within a single network infrastructure. Cisco UC devices can manage all three types of traffic and interface with all standard network protocols. The new way to supply UC functionality to company customers is through Cisco IP Communications. Cisco UC provides a coordinated release of an integrated set of tested, documents, and supported products as a system rather than delivers a collection of disjointed products with individual release dates, test methodology, and documents.
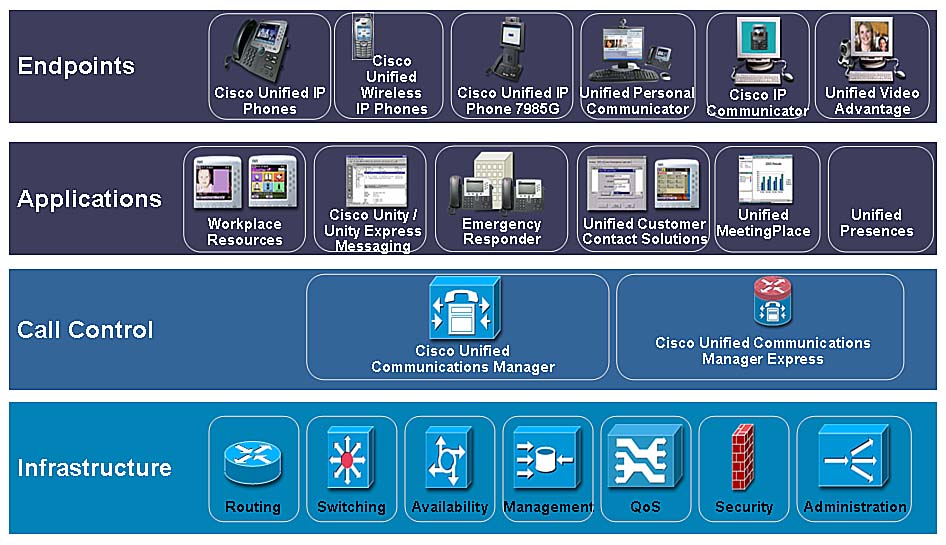
The standard layer components are as follows:
- The layer of infrastructure: the infrastructure includes routers, switches, and voice gateways. Data, voice, and video are transmitted throughout the infrastructure between all network appliances. It offers high availability, management, service quality( QoS), and network security.
- Call control layer: the call control layer provides for dial plan and functionality processing, device management, and administration.
- A CUCM, CUCM express, or CUCM Business Edition (CMBE) may be available for call control. We concentrate on the CUCM product, nearly identical to the Cisco Unified CMBE. Call processing is physically separate from the layer of the infrastructure. Call control for a physical device in Chicago can be executed by a CUCM, Cisco Unified CMBE, or CUCM express in San Jose, for instance.
- The layer of applications: Applications are independent of call control functions and physical voice processing facilities. Applications, including the ones listed here, are integrated with IP so that applications can be located anywhere in the network:
- Cisco Unity, Cisco Unity Express, or Cisco Unity Connections products supply voice mail, integrated messaging, and Unified Messaging applications.
- With the Cisco Unified Contact Center and Cisco Unified Center Express, contact centers of different sizes can be built.
- The Medium to Large Conference Servers supporting video integration from Cisco Unified MeetingPlace and MeetingPlace Express. The product MeetingPlace integrates conferences of the typed lecture with scalable tools for collaboration and control. Small to medium-sized enterprises, the Cisco Unified MeetingPlace Express is positioned. The Cisco Conference Connection server is the successor to MeetPlace Express.
- Cisco Emergency Responder (ER) improves CUCM ‘s current emergency functionality. Cisco ER provides the mobile devices with physical localization updates to guarantee that the PSAP responsible for emergency calls to this site is properly routed to the PSAP. Cisco ER identifies the caller’s location and maps all calls from that physical location to the emergency line identification number (ELIN) using the standard ANI / CLID. The ELIN is registered in ERL( ERL) as part of the PSAP. Implementing these capabilities ensures that legal or regulatory requirements are complied with more effectively and reduces life and responsibility risks related to emergency calls.
- The Cisco Unified Presence server collects information about the user’s availability and communication capabilities and provides this information to user viewers to indicate their status. The user’s communication device availability is included in the status information. The user may, for example, be available via telephone, video, web, or video conferencing.
- The support of third-party applications includes standard protocol interfaces, e.g., Telephony Application Programming Interface( TAPI), Java Telephony Application Programming Interface( JTAPI), Simple Object Access Protocol( SOAP), Q.SIG, H.323, Media Gateway Control Protocol( MGCP), and Session Initiation Protocol( SIP).
- Endpoint layer: the endpoint layer provides the user with applications that are either a Cisco IP Phone, a software-based PC, or a communication client, or a video device. Skinny Client Control Protocol( SCCP)( H.323), MGCP, and SIP-supported by Cisco UC provide multi-protocol support.
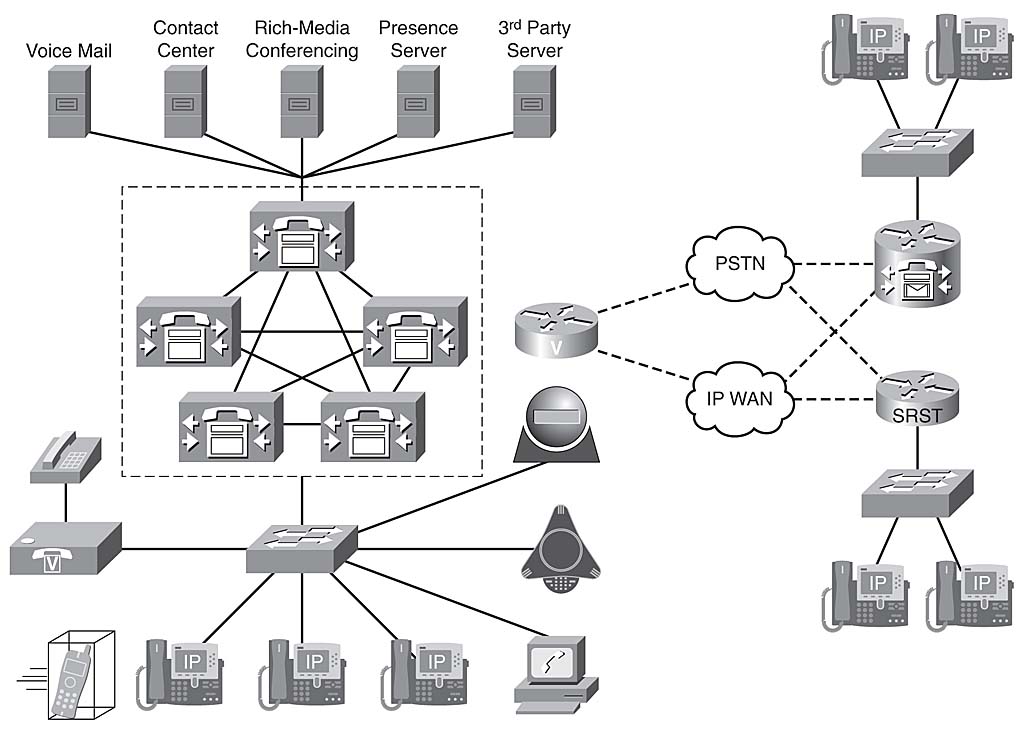
Cisco UC Network
The Cisco UC system provides fully integrated voice, video, and data communications, converging over a single network infrastructure using standard protocols. As demonstrated by the network’s topology, the Cisco UC system offers unparalleled performance and abilities to respond to current and emerging communication needs in the corporate environment.
The UC product suite of Cisco is designed to optimize functionality, reduce the requirements for configuration and maintenance, and interoperability with many different applications. This feature ensures that quality, QoS, and security are highly available.
In Cisco UC, the following major communications technologies are integrated:
- IP phone: IP phone technology is the transmission of voice communications through a network using IP standards. IP telephone: Cisco UC offers a wide range of hardware and software devices such as call processing agents, IP-telephones, voice-messaging systems, video devices, conferencing, and many more.
- Customer contact center: The Cisco Unified Contact Center products combine strategy and architecture to revolutionize telephone settings. By enabling organizations to draw services from a broader range of resources, the Cisco Unified Contact Center promotes effective and efficient customer communications across large networks. These resources include access to a large pool of agents and various communication channels and tools for customer support.
- Video Telephony: The products Cisco Unified Video Advantage enable using the same IP network and call processing agent as Cisco UC in real-time video communication and collaboration. No special end-user training is required for Cisco Unified Video Advantage. Cisco Unified Video Advantage video calling is as simple as dialing a telephone number.
- Conferencing with rich media: Cisco Unified ConferencePlace provides the virtual meeting environment for voice, video, and web conferences with an integrated set of IP- based tools.
- Applications from third parties: Cisco collaborates with leading companies in the widest range of innovative third-party IP communication applications and solutions that focus on critical business needs, such as messaging, customer service, and workforce optimization.
Functions of CUCM
CUCM extends business telephone and packet network device functions. CUCM Cisco IP Telephony devices, media processing devices, VoIP gateways, and multimedia applications include these telephony network devices. Additional services in data, voice, and videos, such as converged messaging, multimedia conferences, collaborative contact centers, and interactive multimedia response systems, interact via CUCM application programming interface (API) and IP-telephony solution.
CUCM provides the following functions:
- Call processing: Call processing refers to the entire process of making, routing, and terminating calls, including all processes of accounting and statistical collection.
- Signaling and control of devices: CUCM establishes all the signal connections between call endpoints and directs devices such as telephones, gateways, and conference bridges to connect and tear down streaming. Call control and call setup/call teardown signals are also called.
- Administration of the dial plan: the dial plan is a set of configurable lists for call routing that CUCM uses. CUCM digitally analyzes all calls. Users can create scalable dial plans through CUCM.
- Administration of phone characteristics: CUCM extends to IP phones and gateways services such as holding, transfer, forwarding, conference, speed dialing, redial and call- parks.
- CUCM uses its own database to store information for its users. Directory Services: Locally or in an external directory, user authentication is carried out. Centralized user management is possible through directory sync. Directory synchronization allows CUCM in a corporate directory to enhance user configuration. Supported directory integrations are Microsoft Active Directory. The Local CUCM database component of the IBM Informix Database Server (IDS) is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) compliant database.
- External application interface: CUCM provides an external program interface for Cisco IP SoftPhone, Cisco IP Communicator, Cisco Unified IP Interactive Voice Response( IP IVR), Cisco Personal Assistant, Unified Personal Communicator, and CUCM Attendant Console.
- Backup and restore tools: CUCM provides a DRS to backup and restore the CUCM settings database. The Call Data Database( CDR), Call Management Records( CMR), and the Analysis and CAR( CDR) database also are supported by the DRS system.
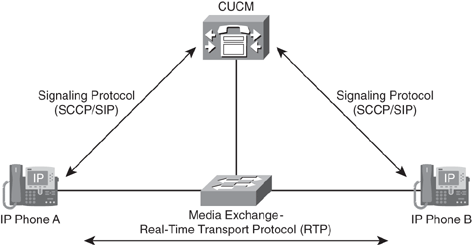
CUCM Signaling and Media Paths
CUCM uses SIP or SCCP to communicate with Cisco IP Phones for call set up, teardown, and supplementary service work. Use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) to deliver audio; after a call has been made, media exchange occurs directly between the Cisco IP Phones across the IP network. After the call has been set up, CUCM is not involved in a call. If the CUCM server were unplugged during the call period, users would never notice it unless they were trying to use a feature on the phone. CUCM is only involved in the setting up, teardown, and functionality of the call. If the CUCM server that installed the call were down, end users would see a message on the LCD screen of the IP phone that read “CM Down, Features Disabled. “
At the start of a call, an IP phone user A collects the handset and sends a message to CUCM, which tells CUCM it has gone off the hook. CUCM answers this stimulus by answering a message that the device plays a dial-tone file stored in the phone’s flash memory. The user listens to the dial tone on phone A and begins to dial phone B. SCCP phones send their numbers to CUCM when pressed, while SIP phones send dialed numbers by default into a single message (signaling). SIP phones have options for using SCCP (keypad mark-up language[ KPML] and dial rules) similar to SCCP phones. CUCM carries out digital analysis of the dialed digits. When a match is detected, CUCM routes the call according to its setup. If a match is not found in CUCM, the caller will receive a reorder tone.
CUCM reports the ringback calling party so that the user hears the ringback tone at Phone A. CUCM also signals the ringdown tone to the destination phone. Further information on the calls and the party name and number are provided to the telephones. Phone A displays the name and number of the target device, and Phone B shows the name and number of the calling party.
When the phone B user accepts the call, CUCM sends a message to the device to inform the IPv4 socket of information that should be contained for the duration of a call( IPv4 address and port number). The RTP media path opens between both phones directly.
Cisco IP Telephones do not require further communication with CUCM until a feature like a call transfer, a call conferencing, or call termination is invoked by either phone.
Do you want to know how your phone system is performing?
If you are looking for a way to monitor the performance of your Cisco Call Manager, then look no further! We provide everything you need in one simple package that will be easy to install and use. There’s no other service like it out there! It’s not just an amazing product but also an incredible experience you can have every day of your life.
Click here right now and sign up for a free trial of PBXDom Call Analytics!